Food chains food webs and energy pyramid worksheet answers key – Embarking on a journey into the intricacies of food chains, food webs, and the energy pyramid, this guide unveils the intricate dynamics that govern the transfer of energy within ecosystems. Delving into the depths of these concepts, we will unravel the complexities that underpin the stability and resilience of our natural world.
Food chains and food webs, intricate tapestries woven by the interdependence of species, provide a glimpse into the interconnectedness of life. The energy pyramid, a towering testament to the laws of thermodynamics, illuminates the hierarchical flow of energy through ecosystems.
Together, these concepts form the cornerstone of ecological understanding, shaping the very fabric of our planet’s biodiversity.
Food Chains and Food Webs: Food Chains Food Webs And Energy Pyramid Worksheet Answers Key
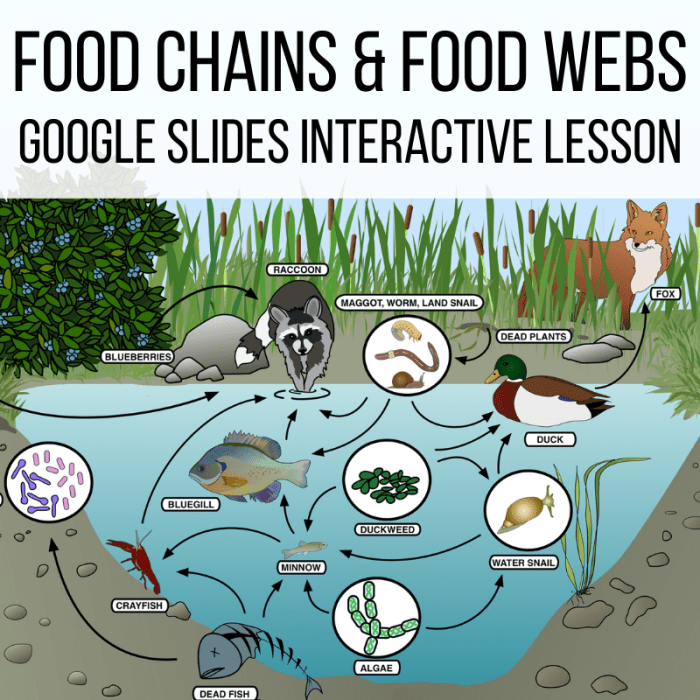
Food chains and food webs are fundamental concepts in ecology that describe the feeding relationships between organisms within an ecosystem. They help us understand the flow of energy and matter through different trophic levels, providing insights into ecosystem structure and dynamics.
Food Chains
A food chain is a linear sequence of organisms, each feeding on the one below it. The first organism in the chain is a producer, which can produce its own food through photosynthesis or chemosynthesis. The remaining organisms are consumers, which rely on other organisms for sustenance.
For example, in a simple food chain, grass (producer) is eaten by a grasshopper (primary consumer), which is then eaten by a snake (secondary consumer), which is finally eaten by a hawk (tertiary consumer).
Food Webs
A food web is a more complex representation of feeding relationships, where organisms are connected through multiple paths. Unlike food chains, food webs depict the interconnectedness and complexity of real-world ecosystems. For example, in a grassland ecosystem, grass may be eaten by grasshoppers, rabbits, and mice, which are in turn preyed upon by snakes, owls, and hawks.
This intricate network of feeding relationships allows for resilience and stability in the ecosystem.
Differences between Food Chains and Food Webs
- Linear vs. Complex:Food chains are linear sequences, while food webs are complex networks.
- Simplicity vs. Realism:Food chains are simplified representations, while food webs provide a more realistic depiction of feeding relationships.
- Flexibility vs. Stability:Food chains are less flexible, while food webs allow for multiple feeding pathways, increasing ecosystem stability.
Energy Pyramid
The energy pyramid is a graphical representation of the flow of energy through different trophic levels in an ecosystem. It is a triangular diagram with the producer level at the base and the top predator level at the apex.
Energy Flow through Trophic Levels, Food chains food webs and energy pyramid worksheet answers key
Energy enters the ecosystem through producers and is transferred to higher trophic levels through consumption. As energy moves up the pyramid, a significant portion is lost as heat due to metabolic processes. Therefore, each trophic level contains less energy than the one below it.
Implications for Ecosystem Stability
The energy pyramid has important implications for ecosystem stability. The narrow base of the pyramid indicates that a small number of producers support a larger number of consumers. This means that disruptions at the producer level can have cascading effects throughout the ecosystem.
Additionally, the pyramid’s shape emphasizes the importance of conserving top predators, as their loss can lead to imbalances in lower trophic levels.
Common Queries
What is the difference between a food chain and a food web?
A food chain is a linear sequence of organisms through which energy flows, while a food web is a more complex network of interconnected food chains.
How does energy flow through the energy pyramid?
Energy flows from producers to consumers, with each trophic level losing approximately 90% of the energy it receives.
What are the implications of the energy pyramid for ecosystem stability?
The energy pyramid highlights the importance of maintaining biodiversity and preventing the loss of species at higher trophic levels, as their absence can destabilize ecosystems.