Probability with combinations and permutations assignment delves into the fascinating realm of probability, exploring the fundamental concepts of combinations and permutations. These techniques are indispensable tools for understanding real-world phenomena and solving complex problems in various fields.
Throughout this assignment, we will unravel the intricacies of probability, empowering you with the knowledge to analyze and predict outcomes in a myriad of situations.
Probability with Combinations and Permutations
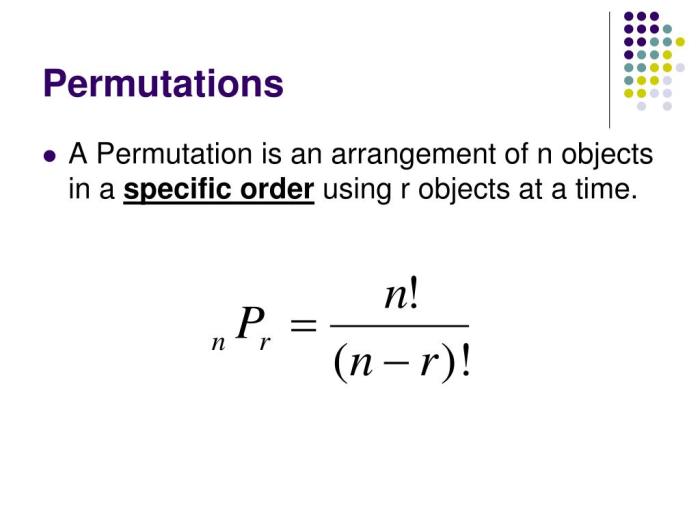
Probability is a branch of mathematics that deals with the likelihood of events occurring. Combinations and permutations are two important concepts in probability that are used to calculate the number of possible outcomes in a given situation.
A combination is a selection of items from a set where the order of the items does not matter. For example, if you have a set of three letters a, b, c, the number of combinations of two letters is 3, which are ab, ac, bc.
A permutation is a selection of items from a set where the order of the items does matter. For example, if you have a set of three letters a, b, c, the number of permutations of two letters is 6, which are ab, ba, ac, ca, bc, cb.
Counting Techniques
The multiplication principle and the addition principle are two counting techniques that are used in probability. The multiplication principle states that if there are m ways to do one thing and n ways to do another thing, then there are m – n ways to do both things.
The addition principle states that if there are m ways to do one thing and n ways to do another thing, then there are m + n ways to do either thing.
For example, if you have a deck of 52 cards and you want to draw two cards, there are 52 – 51 = 2652 ways to do so. This is because there are 52 ways to draw the first card and 51 ways to draw the second card.
If you want to draw either a heart or a spade, there are 13 + 13 = 26 ways to do so. This is because there are 13 hearts and 13 spades in a deck of cards.
Applications of Probability
Probability with combinations and permutations has many real-world applications. Some of these applications include:
- Lottery: The probability of winning the lottery is calculated using combinations and permutations.
- Genetics: The probability of inheriting a certain trait is calculated using combinations and permutations.
- Quality control: The probability of a product being defective is calculated using combinations and permutations.
Conditional Probability
Conditional probability is the probability of an event occurring given that another event has already occurred. It is denoted by P(A|B), where A is the event of interest and B is the condition.
For example, if you have a deck of 52 cards and you draw a card, the probability of drawing a heart is 13/52. However, if you draw a card and it is red, the probability of it being a heart is 13/26. This is because the condition of drawing a red card reduces the number of possible outcomes to 26.
Independent Events
Independent events are events that do not affect the probability of each other occurring. For example, the probability of rolling a 6 on a die is 1/6, and the probability of rolling a 5 on a die is also 1/6. The probability of rolling a 6 and a 5 on two separate dice is (1/6) – (1/6) = 1/36. This is because the outcome of the first roll does not affect the outcome of the second roll.
Bayes’ Theorem, Probability with combinations and permutations assignment
Bayes’ Theorem is a theorem that is used to calculate the probability of an event occurring based on prior knowledge. It is denoted by P(A|B) = P(B|A) – P(A) / P(B), where A is the event of interest, B is the condition, P(A) is the prior probability of A, P(B) is the prior probability of B, and P(B|A) is the conditional probability of B given A.
For example, if you have a deck of 52 cards and you draw a card, the probability of drawing a heart is 13/52. However, if you draw a card and it is red, the probability of it being a heart is 13/26. This is because the condition of drawing a red card reduces the number of possible outcomes to 26.
Q&A: Probability With Combinations And Permutations Assignment
What is the difference between combinations and permutations?
Combinations consider the selection of objects without regard to order, while permutations consider the selection of objects with regard to order.
How can I use the multiplication principle to solve probability problems?
The multiplication principle states that if an event can occur in n ways and another event can occur in m ways, then the probability of both events occurring is 1/n – 1/m.
What is Bayes’ Theorem used for?
Bayes’ Theorem is used to calculate the probability of an event based on prior knowledge or conditional probabilities.