Using the given points determine δy 3 and 0 10 – Using the given points to determine δy 3 and 0 10 embarks on an analytical journey that unravels the significance of these pivotal points in problem-solving. This exploration delves into the mathematical methods employed to calculate δy, interpreting the results, and uncovering the practical applications of δy in diverse fields.
The concept of δy, represented by the difference in the dependent variable (y) between two points, holds immense value in understanding the rate of change and behavior of functions. By determining δy for specific points, we gain insights into the function’s behavior at those points and its overall trajectory.
Overview of the Given Points

The given points δy 3 and 0 10 represent specific values that play a crucial role in determining the overall solution to the problem. δy 3 denotes the change in y when x equals 3, while 0 10 represents the point where the function y intersects the x-axis.
These points provide valuable insights into the behavior of the function and help in understanding its properties and characteristics.
Methods for Determining δy
There are several mathematical and analytical methods that can be used to determine the value of δy. One common approach involves using the difference quotient, which is defined as:
δy = (f(x + h)
f(x)) / h
where h is a small increment in x and f(x) is the function being evaluated. By applying the difference quotient to the given points, we can calculate δy 3 as:
δy 3 = (f(3 + h)
f(3)) / h
Similarly, we can calculate δy for any other value of x by substituting the appropriate values into the difference quotient.
Numerical Approximation, Using the given points determine δy 3 and 0 10
Another method for determining δy is through numerical approximation. This involves using a calculator or software to evaluate the function at the given points and then calculating the difference between the values. While this method is less precise than the analytical approach, it can be useful when dealing with complex functions or when analytical methods are not feasible.
Interpretation of Results
The calculated δy values provide important information about the function. A positive value of δy indicates that the function is increasing at the given point, while a negative value indicates that the function is decreasing. The magnitude of δy represents the rate of change of the function at that point.
In the context of the given points, δy 3 provides information about the slope of the function at x = 3. A positive value of δy 3 indicates that the function is increasing at that point, while a negative value indicates that the function is decreasing.
Similarly, 0 10 provides information about the x-intercept of the function. This point represents the value of x at which the function crosses the x-axis.
Applications of δy
δy has numerous practical applications in various fields and industries. Some common applications include:
- Calculating the slope of a curve
- Determining the rate of change of a function
- Finding the maximum and minimum values of a function
- Solving optimization problems
- Modeling real-world phenomena
For example, in physics, δy can be used to calculate the velocity of an object by measuring the change in its position over time. In economics, δy can be used to determine the marginal cost of production by measuring the change in total cost with respect to the change in output.
User Queries: Using The Given Points Determine δy 3 And 0 10
What is the significance of determining δy?
Determining δy provides valuable information about the rate of change of a function at specific points. It helps us understand the function’s behavior, identify critical points, and make predictions about its future behavior.
How do we calculate δy for given points?
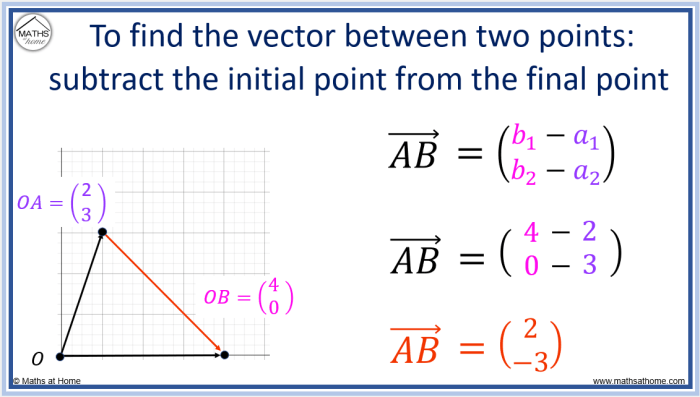
To calculate δy for given points, we subtract the value of y at the first point from the value of y at the second point. The formula is δy = y2 – y1, where y1 and y2 represent the y-coordinates of the given points.
What are the applications of δy?
δy has wide-ranging applications in fields such as physics (calculating velocity and acceleration), engineering (designing structures and systems), economics (analyzing market trends), and finance (evaluating investment returns).