Classify the following compounds as having covalent or ionic bonds – The classification of compounds as covalent or ionic is a fundamental concept in chemistry, providing insights into their bonding characteristics and properties. This guide delves into the distinction between these two bond types, exploring their key features and providing a systematic approach to their identification.
Understanding the nature of chemical bonds is crucial for comprehending the behavior and applications of compounds in various fields. This guide will equip readers with the knowledge and tools necessary to classify compounds accurately and gain a deeper understanding of their chemical properties.
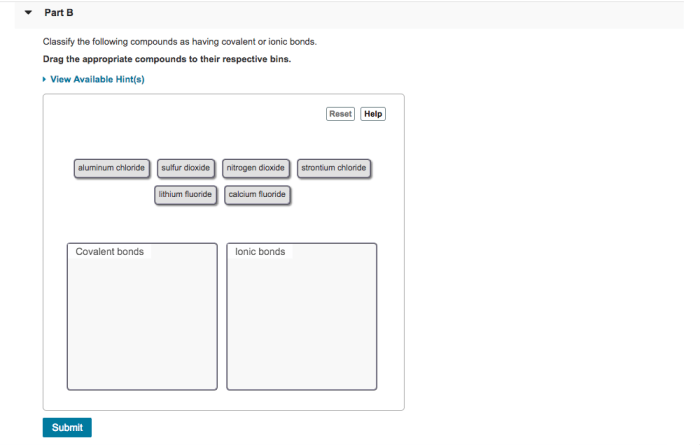
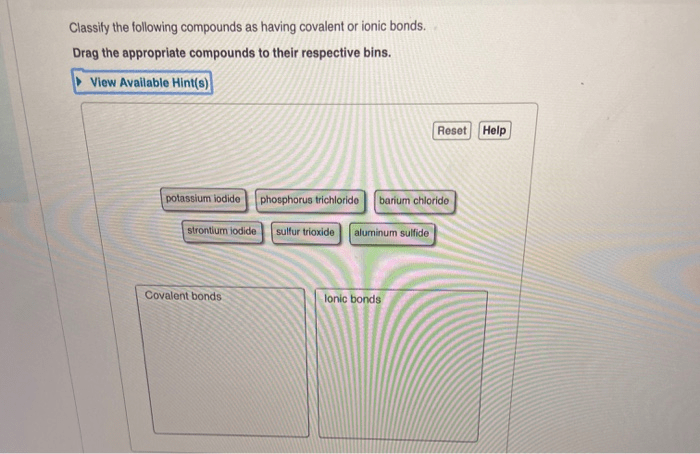
Classify the Following Compounds as Having Covalent or Ionic Bonds
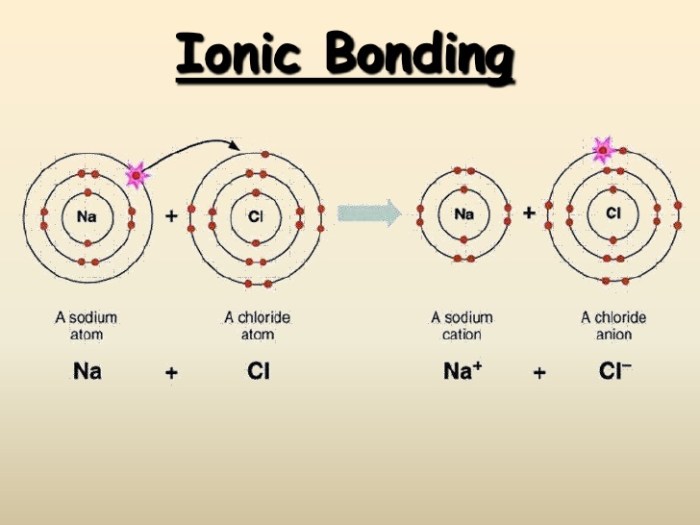
Chemical bonds are the forces that hold atoms together to form molecules and compounds. There are two main types of chemical bonds: covalent bonds and ionic bonds. Covalent bonds are formed when atoms share electrons, while ionic bonds are formed when atoms transfer electrons from one atom to another.
The type of chemical bond that forms between two atoms depends on the electronegativity of the atoms. Electronegativity is a measure of how strongly an atom attracts electrons. The more electronegative an atom, the more strongly it attracts electrons. If two atoms have a large difference in electronegativity, then the more electronegative atom will tend to pull electrons away from the less electronegative atom, forming an ionic bond.
If two atoms have a small difference in electronegativity, then they will tend to share electrons, forming a covalent bond.
Examples of Covalent and Ionic Compounds, Classify the following compounds as having covalent or ionic bonds
Here is a table with examples of covalent and ionic compounds:
| Covalent Compounds | Ionic Compounds |
|---|---|
| H2O | NaCl |
| CH4 | MgO |
| CO2 | CaCl2 |
Covalent compounds are typically formed between non-metals. Ionic compounds are typically formed between a metal and a non-metal.
Methods for Determining Bond Type
There are a number of methods that can be used to determine the bond type of a compound. One method is to look at the electronegativity of the atoms involved. If the atoms have a large difference in electronegativity, then the bond is likely to be ionic.
If the atoms have a small difference in electronegativity, then the bond is likely to be covalent.
Another method for determining bond type is to look at the physical properties of the compound. Ionic compounds are typically solids at room temperature, while covalent compounds can be solids, liquids, or gases at room temperature. Ionic compounds are also typically soluble in water, while covalent compounds are typically insoluble in water.
Applications of Covalent and Ionic Compounds
Covalent and ionic compounds have a wide range of applications in various fields. Covalent compounds are used in a variety of products, including plastics, fuels, and pharmaceuticals. Ionic compounds are used in a variety of products, including fertilizers, detergents, and batteries.
The specific properties of covalent and ionic compounds make them suitable for different applications. For example, the strong bonds in covalent compounds make them ideal for use in plastics and other materials that need to be strong and durable. The solubility of ionic compounds in water makes them ideal for use in fertilizers and detergents.
FAQ Compilation: Classify The Following Compounds As Having Covalent Or Ionic Bonds
What is the primary difference between covalent and ionic bonds?
Covalent bonds involve the sharing of electrons between atoms, while ionic bonds result from the transfer of electrons from one atom to another, creating oppositely charged ions.
How can I determine the bond type of a compound?
Several methods can be used to determine bond type, including electronegativity difference, solubility, and conductivity.
What are some examples of covalent and ionic compounds?
Covalent compounds include water (H2O), methane (CH4), and carbon dioxide (CO2), while ionic compounds include sodium chloride (NaCl), potassium iodide (KI), and calcium oxide (CaO).