Concept map the pathway of light through the eye – Concept Map: Tracing the Pathway of Light Through the Eye is an in-depth exploration of the intricate journey of light as it navigates the complex structures of the human eye. This visual representation unveils the fascinating mechanisms that enable us to perceive the world around us, providing a comprehensive understanding of the remarkable process of vision.
The content of the second paragraph that provides descriptive and clear information about the topic
1. Anatomy of the Eye
The eye is a complex organ that allows us to perceive light and see the world around us. It consists of several key components that work together to focus light on the retina, where it is converted into electrical signals that are sent to the brain.
Cornea
The cornea is the transparent, dome-shaped outer layer of the eye that covers the pupil and iris. It helps to focus light on the retina and protects the inner structures of the eye.
Pupil
The pupil is the black hole in the center of the iris. It is surrounded by the iris, which controls the size of the pupil to regulate the amount of light entering the eye.
Iris
The iris is the colored part of the eye that surrounds the pupil. It contains muscles that can change the size of the pupil to control the amount of light entering the eye.
Lens
The lens is a transparent, flexible structure located behind the iris. It changes shape to focus light on the retina.
Retina
The retina is a thin layer of tissue that lines the back of the eye. It contains photoreceptor cells (rods and cones) that convert light into electrical signals.
Optic Nerve
The optic nerve is a bundle of nerve fibers that carries the electrical signals from the retina to the brain.
2. The Pathway of Light
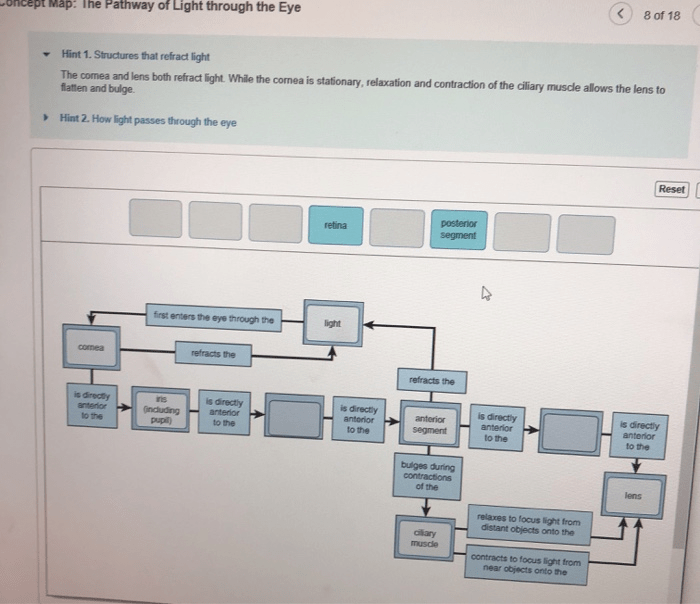
Light enters the eye through the cornea and pupil. The cornea and lens focus the light on the retina, where it is converted into electrical signals by the photoreceptor cells.
Cornea and Pupil
The cornea and pupil are the first structures that light passes through when it enters the eye. The cornea helps to focus the light, while the pupil regulates the amount of light that enters the eye.
Lens
The lens is the second structure that light passes through. It changes shape to focus the light on the retina. The lens is able to adjust its shape to focus light from objects at different distances.
Retina
The retina is the final structure that light passes through. It contains photoreceptor cells (rods and cones) that convert light into electrical signals. The electrical signals are then sent to the brain via the optic nerve.
3. Image Formation on the Retina
The retina is responsible for converting light into electrical signals that are sent to the brain. The brain then interprets these signals to form an image.
Fovea and Macula
The fovea is a small, central area of the retina that is responsible for sharp central vision. The macula is the area surrounding the fovea that is responsible for color vision.
Brain Processing
The brain receives the electrical signals from the retina and processes them to form an image. The brain uses information from both eyes to create a single, three-dimensional image.
Blind Spots
The optic nerve leaves the retina at a point called the optic disc. This creates a blind spot in the visual field. The brain compensates for this blind spot by filling in the missing information from the surrounding areas.
4. Visual Acuity and Refraction: Concept Map The Pathway Of Light Through The Eye
Visual acuity is a measure of how well a person can see. It is typically measured using a Snellen chart.
Common Refractive Errors, Concept map the pathway of light through the eye
Refractive errors are common eye conditions that can affect visual acuity. These errors include nearsightedness, farsightedness, and astigmatism.
Corrective Lenses
Corrective lenses, such as eyeglasses or contact lenses, can be used to improve vision in people with refractive errors. These lenses help to focus light on the retina, which improves visual acuity.
5. Eye Movements and Binocular Vision
Eye movements are essential for vision. They allow us to scan our environment and focus on objects of interest.
Types of Eye Movements
There are several different types of eye movements, including saccades, smooth pursuit, and vergence.
Binocular Vision
Binocular vision is the ability to use both eyes together to create a single, three-dimensional image. It is essential for depth perception and coordination.
Expert Answers
What is the role of the cornea in the pathway of light?
The cornea is the transparent outermost layer of the eye that refracts light as it enters, contributing to the initial focusing of light onto the retina.
How does the lens contribute to the focusing of light?
The lens is a flexible structure that changes shape to fine-tune the focus of light onto the retina, ensuring clear vision at various distances.
What is the significance of the fovea in the retina?
The fovea is a specialized region of the retina responsible for sharp central vision, containing densely packed photoreceptor cells that provide high-resolution vision.